AuthorPeter Oakes is an experienced anti-financial crime, fintech and board director professional. Archives
January 2025
Categories
All
|
Back to Blog
Irish Bank, Bank of Ireland, fined €1,660,000 over cyber-fraud and misleading the Irish Regulator28/7/2020 Enforcement Action Notice: The Governor and Company of the Bank of Ireland fined €1,660,000 and reprimanded by the Central Bank of Ireland for regulatory breaches causing loss to a client and for misleading the Central Bank in the Central Bank in the course of the investigationSummary:Here's a blueprint for inviting an enforcement action for cyber-fraud & misleading your regulator arising from Bank of Ireland's fine €1,660,000 announced today. [Linkedin Post Here] What did Bank of Ireland do wrong?: 1) failed to implement sound administrative procedures & internal control mechanisms in respect of third party payments. 2) failed to introduce adequate organisational arrangements around third party payments to minimise the risk of loss of client assets as a result of fraud. 3) failed to establish, implement & maintain systems & procedures adequate to safeguard the security, integrity & confidentiality of client bank account details. 4) failed to establish, implement & maintain adequate internal control mechanisms designed to secure compliance with its reporting obligations pursuant to Sec. 19 of the Criminal Justice Act 2011. 5) failed to monitor adequacy & effectiveness of the measures & procedures put in place & the actions taken to address any deficiencies in respect of third party payments. 6) failed to be open & transparent, having the effect of misleading the Central Bank in the course of the investigation. Facts of Matter according to Central Bank of Ireland:On 27 July 2020, the Central Bank of Ireland (the Central Bank) reprimanded and fined The Governor and Company of the Bank of Ireland (BOI) for five breaches of the European Communities (Markets in Financial Instruments) Regulations 2007 (the MiFID Regulations) committed by its former subsidiary, Bank of Ireland Private Banking Limited (BOIPB). BOI has admitted the breaches, which vary in length from one to ten years.
In line with its published Sanctions Guidance, the Central Bank has determined the appropriate fine to be €2,370,000, which has been reduced by 30% in accordance with the settlement discount scheme provided for in the Central Bank’s Administrative Sanctions Procedure. The Central Bank’s investigation arose from a cyber-fraud incident that occurred in September 2014 (the Incident). Acting on instructions from a fraudster impersonating a client, BOIPB made two payments to a third party account totalling €106,430: one from a client’s personal current account, the other from BOIPB’s own funds. BOIPB immediately reimbursed the client. During a Full Risk Assessment of BOIPB in 2015, the Central Bank discovered a reference to the Incident in an operational incident log. BOIPB had not reported the cyber-fraud to An Garda Síochána, and only did so at the request of the Central Bank over one year after the Incident. The Central Bank’s investigation found serious deficiencies in respect of third party payments, including:
BOIPB’s failure to be open and transparent had the effect of misleading the Central Bank in the course of the investigation. BOIPB failed for a period of 19 months to disclose to the Central Bank an internal report, commissioned following the Incident, which identified ongoing systemic control failings in the processing of third party payments. During that same period, BOIPB strenuously denied the existence of any such failings to the Central Bank in response to the investigation. BOIPB’s conduct materially added to the time it took to investigate this case. This is one of two aggravating factors in this case; the other being the excessive amount of time it took BOIPB to fully remediate the relevant deficiencies. Remediation in relation to third party payment processes took place in February 2016, 17 months after the Incident, and then only following the Central Bank’s intervention. In August 2016, the Central Bank determined that a Risk Mitigation Programme (RMP) relating to third party payment processes was completed. The Central Bank’s Director of Enforcement and Anti-Money Laundering, Seána Cunningham, said: “The Central Bank has a clear expectation that firms are alert to the real and increasing risks from cyber-fraud to the security of their clients’ deposits and confidentiality of their clients’ financial information, and put in place appropriate safeguards to protect their clients accordingly. This is the second time the Central Bank has imposed a sanction on a firm where a client has suffered a loss from cyber-fraud as a direct result of the firm’s regulatory failings. BOIPB’s failure to put appropriate safeguards in place exposed BOIPB and its clients to the serious and avoidable risk of cyber-fraud. That risk crystallised twice. BOIPB then failed to report the cyber-fraud to An Garda Síochána, which is a serious matter. Reporting illegal activity is essential in the fight against financial crime. This case should serve to highlight to all firms the importance of ongoing vigilance in the area of cyber security. The Central Bank expects all firms to consider, identify and manage operational and cyber risks and ensure that their staff receive appropriate training tailored to the risks associated with their duties and responsibilities. The Central Bank expects pro-active engagement from regulated entities – that extends from self-reporting through remediation and full cooperation with the investigation. The excessive time taken by BOIPB to remediate identified deficiencies and the failure to be fully transparent and open in the context of the Central Bank’s investigation were aggravating features in this case.” BACKGROUND Founded in 1989, BOIPB was first authorised as a “section 10 investment business firm” under the Investment Intermediaries Act, 1995 (the 1995 Act) on 26 May 2000. This authorisation was subsequently transferred to an authorisation under the MiFID Regulations on 1 November 2007. At the time of the cyber-fraud, BOIPB was an independently regulated MiFID firm and its primary activity was to provide investment services to high net worth individuals who had investable assets in excess of €1,000,000. In addition, BOIPB provided a full range of banking services to its clients (lending, deposit taking and day-to-day current account banking) as a deposit agent of BOI. Since 1 September 2017, BOIPB is no longer a MiFID firm and is now a business unit within the Retail Division of BOI. The unit retains the name Bank of Ireland Private Banking as a trading name of the Governor and Company of the Bank of Ireland. Its services are authorised by the Central Bank of Ireland under the licence of BOI, a regulated financial service provider for the purposes of the Central Bank Act 1942. BOIPB’s audited financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2016, the last year it existed as a separate entity, reported operating income of €19,867,000. THE CYBER-FRAUD Third party payment instructions were processed by BOIPB with particular reference to a procedure called the Third Party Payments Procedure (the TPPP), which outlined steps to be followed to verify a client’s identity before processing a third party payment instruction. BOIPB processed two separate payment instructions received in September 2014, purportedly from a client (the Client), which in fact were sent by a cyber-fraudster (the Fraudster) who had hacked the Client’s e-mail account. This led to two transfers totalling €106,430 to be transmitted to a corporate bank account at a UK bank. The first transfer was drawn from the Client’s current account, and the second transfer was drawn, at the instigation and authorisation of BOIPB, from BOIPB’s suspense account because the payment from the Client’s deposit account was rejected due to insufficient funds. The Client made contact with BOIPB and notified it of the fraud on 30 September 2014, on receipt of an e-mail from BOIPB indicating recent communications (which were unfamiliar to the Client). The Client was immediately reimbursed by BOIPB. To facilitate the instructions received from the Fraudster, BOIPB staff, in breach of BOIPB’s policies and procedures:
The Fraudster used the following tactics:
PRESCRIBED CONTRAVENTIONS The Central Bank investigation identified the following contraventions: Contravention 1 BOIPB breached Regulation 33(1)(f)(i) of the MiFID Regulations between 1 November 2007 and August 2016 by failing to implement sound administrative procedures and internal control mechanisms in respect of third party payments. The Central Bank’s investigation found that the TPPP was wholly inadequate for the purposes of safeguarding client deposits when processing third party payments. In particular, key procedural, security and authorisation steps were not outlined in the document. Staff did not receive adequate training on the processing of third party payments to ensure they were fully aware of how to safely process these payments. Contravention 2 BOIPB breached Regulation 160(2)(f) of the MiFID Regulations between 1 November 2007 and August 2016 by failing to introduce adequate organisational arrangements around third party payments to minimise the risk of loss of client assets as a result of fraud. The serious weaknesses in the process around third party payments, which had existed for some time, should have been known to management through proper governance, oversight and monitoring. There was no monitoring of third party payments by the first or second lines of defence. Furthermore, the recommendations of the first internal report commissioned by BOIPB in relation to this matter, dated December 2014, were not acted on. Similar weaknesses were identified in a second internal report in January 2016. Remediation of the issues identified in both reports did not take place until February 2016. Contravention 3 BOIPB breached Regulation 34(3)(a) of the MiFID Regulations between 1 November 2007 and 2 January 2018 by failing to establish, implement and maintain systems and procedures adequate to safeguard the security, integrity and confidentiality of client bank account details. The investigation found that for the purposes of customer service, BOIPB staff frequently engaged with private clients through e-mail. E-mail communication, because it is more vulnerable to infiltration by fraudsters than other forms of communication, needs to incorporate additional checks before being acted upon. By failing to identify and provide for this, BOIPB failed to safeguard the security, integrity and confidentiality of information relating to client bank accounts. Contravention 4 BOIPB breached Regulation 34(1)(c) of the MiFID Regulations between 30 September 2014 and 16 December 2015 by failing to establish, implement and maintain adequate internal control mechanisms designed to secure compliance with its reporting obligations pursuant to Section 19 of the Criminal Justice Act 2011. BOIPB reported the Incident to its Group Financial Crime Unit (GFCU) on 1 October 2014. GFCU, on behalf of BOIPB, did not report the Incident to An Garda Síochána until December 2015, on the instigation of the Central Bank. Contravention 5 BOIPB breached Regulation 35(2)(c) of the MiFID Regulations by failing to comply with Regulation 34(4) between November 2013 and December 2016 because, for that period, BOIPB’s Compliance function failed to monitor, and on a regular basis to assess the adequacy and effectiveness of the measures and procedures put in place and the actions taken to address any deficiencies in respect of third party payments. The TPPP included a requirement that ad-hoc monitoring of third party payments be carried out by the Compliance function. The investigation found that throughout the period November 2013 to May 2016, no ad-hoc monitoring of third party payments was in fact carried out. This failure persisted despite two internal reports highlighting the absence of monitoring and the systemic non-adherence to the TPPP. BOIPB’S RESPONSE TO THE CYBER-FRAUD AND REMEDIATION The Central Bank expects firms to promptly remediate known deficiencies in their procedures and internal control mechanisms. BOIPB failed to do so. Following the Incident, BOI Group Internal Audit function (GIA) investigated how it had occurred. GIA produced their findings in a report in December 2014, which pointed to systemic failings in the processing of third party payments. GIA strongly recommended that BOIPB carry out sampling to verify the authenticity of other “high-value interpays”. BOIPB failed to do this. GIA further recommended, that, at a minimum, the procedure in place relating to third party payments should be enhanced to clarify roles and responsibilities for authenticating and approving third party payments. Again, BOIPB failed to do this. The procedure remained unchanged until February 2016. In March 2015, BOIPB commissioned a further internal review, this time by BOI Retail Business Assurance (RBA) centred on BOIPB’s procedures for processing third party payments. Separately, following the Full Risk Assessment (the FRA) conducted in 2015, the Central Bank informed BOIPB that improvements in relation to third party payment processes would be part of the subsequent RMP arising from the FRA as the process in place was “not robust enough”. The RMP was issued in February 2016, which set out the Central Bank’s expectations in relation to the actions needed to improve the third party payment process. RBA issued its findings in draft to BOIPB in January 2016 (the RBA Report). Following an assessment of a sample of third party payment records, RBA concluded that the same issues identified in December 2014 persisted, namely that client identification questions were not consistently being asked of clients as well as other deficiencies in the third party payment process. BOIPB updated and revised the TPPP in February 2016. The RBA Report was signed-off in June 2016. In August 2016, the Central Bank determined that the full RMP was completed. BOIPB’S COOPERATION WITH THE CENTRAL BANK The Central Bank expects regulated entities to cooperate in an open manner at all times and to respond to requests promptly, effectively and accurately. When the Central Bank’s investigation commenced in February 2016, BOIPB possessed the RBA Report which contained highly critical findings in relation to the processing of third party payments. As such, it was highly probative to the Central Bank’s investigation. The Central Bank issued a request for records in February 2016. BOIPB should have provided a copy of the RBA Report when it responded to this request in April 2016. BOIPB failed to do so, instead it included one vague narrative reference to a risk assessment of banking activities (making no reference to a “report” or the fact that it related to third party payments specifically) within a document accompanying the records it supplied in response to the Central Bank’s request. BOIPB disclosed the RBA Report to the Central Bank 19 months after the commencement of its investigation in response to a Central Bank statutory request explicitly requiring production of the record BOIPB had described as a “risk assessment”. It was only when the document was disclosed and reviewed that its true nature and content became apparent to the Central Bank. The Central Bank conducted lengthy enquiries as to the circumstances around BOIPB’s failure to promptly disclose the RBA Report and the following arose:
SANCTIONING FACTORS In deciding the appropriate penalty to impose, the Central Bank considered the ASP Sanctions Guidance issued in November 2019. The following particular factors are highlighted in this case. The Nature, Seriousness and Impact of the Contravention
The Conduct of the Regulated Entity after the Contravention Aggravating
Other Considerations
The Central Bank confirms that the investigation is now closed. NOTES
Further information: Media Relations: [email protected] / 01 224 6299 Ewan Kelly: [email protected] / 086 463 9652
0 Comments
Read More
Back to Blog
5 point list of root causes of non-financial risk issuesDownload Westpac's Report released 17 July 2020 - Reassessment of the Culture, Governance and Accountability Remediation Plan Linkedin Post at https://www.linkedin.com/posts/peteroakes_riskculture-riskmanagement-regtech-activity-6689803983407628288-ynbv Here's a good 5 point list of root causes of non-financial risk issues at large systemically important banks & institutions (anywhere in the world). In this case Westpac, arising from a report ordered by the Australian prudential regulator. Applicable to non banks and non systemically important institutions:
With Westpac's CEO responsible for its new initiative "customer outcomes and risk excellence" or CORE, #regtech will need to feature heavily in execution, tracking & learnings. Professor Elizabeth Sheedy, a #riskculture expert saying that the latest report shows too often risk is seen as a handbrake by banks rather than an enabler for long-term success. Westpac "admitted the "culture, governance and accountability program", set up in January 2019 to implement the reforms, "has not delivered sufficient momentum", with many in the bank still do not "fully appreciate the cumulative impact of the issues". Paul McCarthy Westpac culture still 'immature and reactive' 17 July 2020Copyright with Australian Financial Review and James Eyers
Westpac Banking Corp has been forced to launch a new program to attempt to fix its broad risk-management failings, after a reassessment of its culture demanded by Australian Prudential Regulation Authority identified ongoing concerns, including that its non-financial risk culture is still "immature and reactive". The new report identifies a lack of urgency and clarity in Westpac's response to problems it identified in a 2018 self-assessment of governance, which were exacerbated when AUSTRAC dropped a bombshell case last November that triggered the departures of the bank's CEO and chairman. The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority insisted on the reassessment because it was concerned Westpac was not tackling the root causes of its failings when it read AUSTRAC's statement of claim. The latest investigation found Westpac is still "overly complex, which results in confusion around accountability and challenges in execution". The shortcomings identified in the report, which was sent to all of Westpac's 35,000 staff on Friday morning, found Westpac's organisational structure created complexity, and its 'three lines defence' model, which is supposed to prevent risks materialising, "is not well understood or embedded". The report highlights a "shortfall in sufficient non-financial risk-management capability" and says that even though Westpac has made various changes to respond to issues, "what is required is a program of deeper change". It criticised an ongoing blame game, stating a priority for its work on culture "will be to strengthen psychological safety" for staff after the reassessment found "in some situations leaders had reacted to incidents with a focus on who is to blame rather than what to learn". Many of the same failings were identified in the bank's self-assessment for APRA in 2018, after all banks were asked to audit themselves against the prudential regulator's expectations for fixing widespread cultural problems at Commonwealth Bank of Australia. The Hayne royal commission should also have emphasised the urgency of repairing culture to meet community expectations and restore trust. But Westpac recognised on Friday the changes it has been making to respond to the 45 recommendations set out in its 2018 self-assessment had been "incremental". It admitted the "culture, governance and accountability program", set up in January 2019 to implement the reforms, "has not delivered sufficient momentum". It said many in the bank still do not "fully appreciate the cumulative impact of the issues". “Our reassessment confirms that our management of non-financial risk is currently not at the standard we set for ourselves," said Westpac CEO, Peter King, releasing the 50-page report to the ASX. “It is clear we have more to do to address these shortcomings, including improving our risk management capability and risk culture which is not where we want it to be." APRA is continuing to investigate possible breaches of the Banking Act by Westpac, including the speed at which it has rectified issues identified by AUSTRAC. APRA has already imposed a $1 billion capital penalty on the bank to reflect its "heightened operational risk profile". At the CORE Westpac on Friday announced it would initiate a multi-year, multi-million dollar program, which it is calling "customer outcomes and risk excellence" (CORE). Mr King said he would be accountable for its delivery. The reassessment said Mr King, who replaced Brian Hartzer as CEO, and the Westpac board, now led by John McFarlane who took the reins from Lindsay Maxsted, need to take more responsibility and set a proper "direction and tone" about the importance of the measures. The report – which was conducted by Westpac management and a team from consultants Oliver Wyman together with assurance oversight by another consulting firm, Promontory – pointed to five ongoing "root causes" of Westpac's travails. These are: an organisational construct that creates complexity; an "immature and reactive" risk culture in non‑financial risk management; a 'three lines of defence model' that is not well understood or embedded among bank staff; the lack of sufficient non-financial risk management capability; and challenges in execution and staying the course. "Westpac does not underestimate both the magnitude of the changes that are required and the effort involved." Professor Elizabeth Sheedy, a risk culture expert from Macquarie University, said the latest report shows too often risk is seen as a handbrake by banks rather than an enabler for long-term success. "For me it all comes back to excessive focus on short-term profits which is driven by short-term cash bonuses," she said. "There is also a massive shortage of qualified and experienced risk and compliance executives across the industry. Institutions tend to want to keep budgets very tight when it comes to resourcing risk and compliance, which sends a message about organisational priorities." It is expected that Westpac will look to make additional cost savings in order to pay for additional investment that will be required to improve risk systems. The report was released after Mr McFarlane warned in an interview with the Financial Review on Friday that excessive financial regulation could make it more difficult for banks to lend and hamstring the economic recovery. Westpac has been negotiating with AUSTRAC over a potential settlement of the anti-money laundering case, with the financial crimes regulator due to file an amended statement of claim next month to incorporate broader allegations that the bank should have suspected another 270 customers were paedophiles. It is also waiting for a decision from the Australian Securities and Investments Commission on whether it will appeal the bank's responsible lending victory in the full Federal Court last month to the High Court. James Eyers writes on banking, fintech and technology. Based in our Sydney newsroom, James is a former Legal Affairs and Capital editor for the Financial Review Connect with James on Twitter. Email James at [email protected] Source: https://www.afr.com/companies/financial-services/westpac-culture-still-immature-and-reactive-20200717-p55cxa
Back to Blog
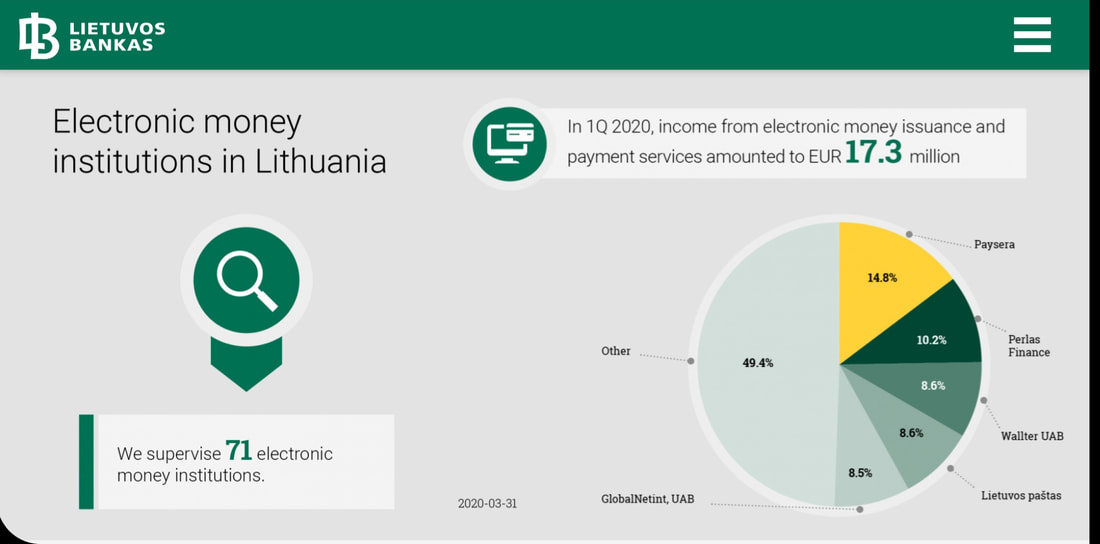
If you use all or any part of this blog, please ensure you cite and credit CompliReg and Peter Oakes in your re-use of this blog. Another electronic money institution (EMI) fined and sanctioned in Lithuania for anti-money laundering regulatory requirements and in this case also for an equity capital requirement failure. While the case is worth noting for both aspects, it is particularly so because across Europe, following the collapse of Wirecard, there will be continuing heightened awareness of both safeguarding and capitalisation of regulated EMIs and payment institutions (PIs). The case also makes known that the BoL is conducting targeted inspections of EMIs across a range of themes. In our previous blog, 2 June 2020, on the Lithuanian Central Bank (Bank of Lithuania / BoL) giving banks guidelines on opening accounts for electronic money institutions (EMIs) and payment institutions (PIs) Peter Oakes noted recent examples of fines against EMIs/PIs including failures to comply with requirements for: (i) anti-money laundering; (ii) safeguarding of customer funds; and (iii) segregation of customer funds and; execution of payment transactions. The Bank of Lithuania, which supervises 71 EMIs - which is the largest number of EMIs supervised by an EU financial regulator national competent authority* - has announced that it has taken regulatory action against Via Payments UAB for both: (1) violations of the requirements for prevention of money laundering and terrorist financing (sanctioned with a fine of €120,000 and publicity); and (2) failure to meet the equity capital requirement (sanctioned with publicity only). Via Payments UAB holds an electronic money institution licence, issued on 10 October 2017. As you will see from the graphic below, in addition to BoL supervising 71 EMIs we also learn that Q1 2020 income from EMI and payment services amounted to €17.3 million. Keep reading below for the background to the facts of the Via Payments UAB enforcement action. (1) Background to the money laundering law violations:
The regulatory actions were taken on foot of a "targeted inspection of the electronic money institution Via Payments UAB". During the course of the inspection, the Supervision Service of the BoL identified breaches of the Republic of Lithuania Law on the Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing. In addition to a fine of €120,000, the BoL obligated Via Payments to remedy the deficiencies. BoL says that Via Payments has confirmed that all deficiencies have been remediated. With respect to the money laundering violations, the inspection revealed that:
BoL imposed a fine of €120,000 on Via Payments UAB. As part of its mitigation Via Payments informed the BoL’s Supervision Service that it had already taken measures to strengthen its AML compliance by increasing the number of specialists and improving technological solutions. (2) background to the equity capital requirement failure This regulatory failure came to the attention of the BoL through a separate analysis of the activities of EMIs. Here the Supervision Service of the BoL recorded that Via Payments violated legal acts because as at 31 March 2020 the company “failed to meet the equity capital requirement”. The BoL appears to have place a lot of reliance on the institution having “eliminated the indicated shortcomings without further delay, no interests of their clients have been violated” and therefore BoL “decided to impose a mild enforcement measure by making these infringements public”. * Note that notwithstanding that the UK is in a post-Brexit transition period, it left the European Union on 31 January 2020. Accordingly, Lithuania although it may have fewer EMIs than the UK, it records the largest number of EMIs in the European Union. Sources:
This blog written by Peter Oakes. Peter advises on Lithuanian EMI/PI issues and advised on the authorisation of one Lithuania's first special bank authorisations. If you require a licence to operate in Lithuania, Ireland, Cyprus, Malta or the UK, see our Authorisation Page. We have a great network of experts in each country too, from lawyers, to accountants to technical experts. And get in contact if you have a question about this blog.
Back to Blog
This post first appeared on Peter Oakes's Linkedin Page on 3 July 2020. Given the high level of interest in the post, we have published further information here about the details of the case.
One for the money laundering typologies. This is a useful example to demonstrate how a corrupt solicitor can launder money for clients. ow many times has the compliance department been told "Hey its OK, the client is being vouched for by his / it's lawyer. We don't need proof of source of funds or wealth". Well here's the story of the gangsters' 'go to' solicitor.
Read more at: 2 July 2020 - Solicitor jailed over money laundering links is now struck off 8 January 2019 - 'Go to' solicitor for dodgy property deals jailed for seven years 7 January 2019 - Corrupt lawyer, 39, linked to police killer Dale Cregan is jailed for seven years after he helped a buy-to-let landlord use dirty money to fraudulently build a £10.8m property empire - For advice and training on anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing contact Peter Oakes at CompliReg.
Back to Blog
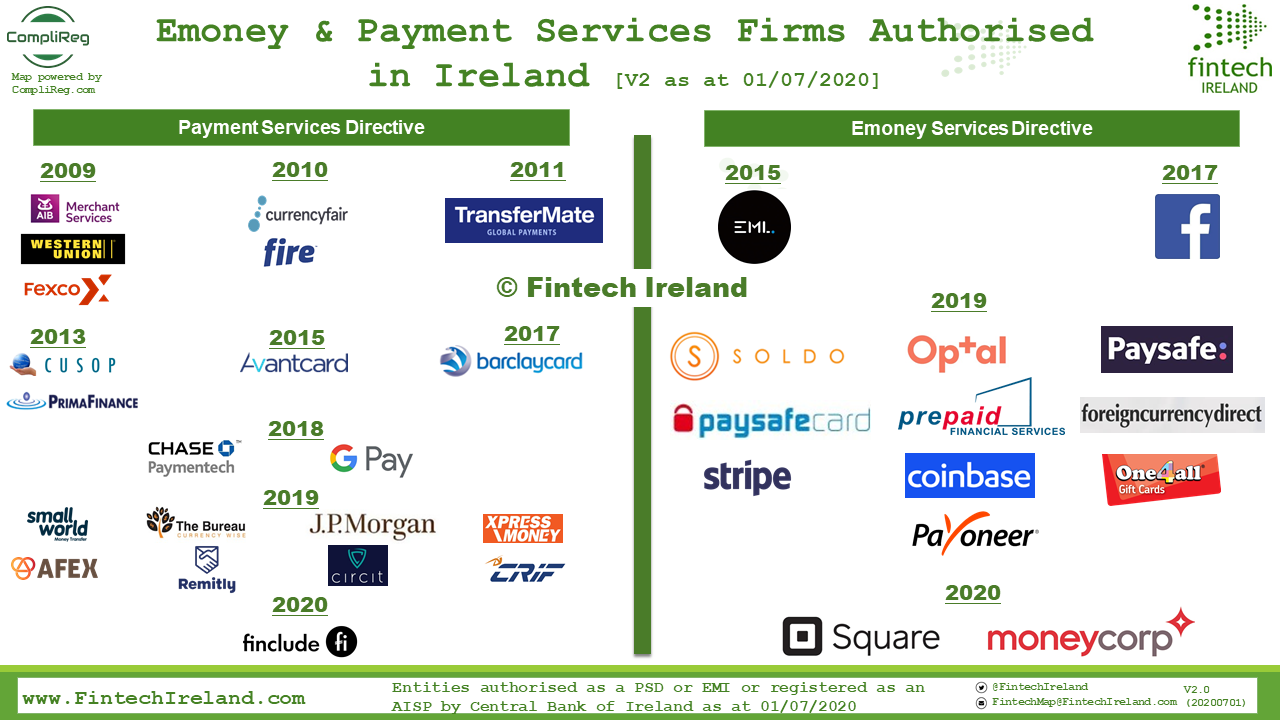
CompliReg is proud to power the Official Fintech Ireland Map 2020. We are now powering the Regulated Fintech Ireland Map version 2 which showcases the regulated payment services directive and electronic money directive firms authorised by the Central Bank of Ireland. Joining this Map in 2020 are the first of two - hopefully many more to come - e-money firms, Squareup International Limited ("Square") and MoneyCorp. Ireland now has:
In addition to issuing emoney, Square is authorised to provide payment services number 3b (execution of payment transactions through a payment card or a similar device) and number 5 (issuing of payment instruments and/or acquiring of payment transactions). Although Moneycorp is yet to appear on the Central Bank of Ireland register, Moneycorp confirmed to us that it is also authorised to provide payment services 3b, 5 and in addition 3c (execution of credit transfers, including standing orders). Moneycorp has been fairly busy. In addition to its emoney authorisation, it also secured a MiFID authorisation. By the way, AFEX which was authorised as payments institution in 2019 also secured a MiFID licence. Expect to see more firms seek both an emoney/payments authorisation together with a MiFID one. Moneycorp’s Dublin office, which opened in 2013, has operated as a branch of its UK regulated entities, saying that as part of Moneycorp’s strategic response to Brexit and wider market developments, it has now secured its e-money and MiFID licences from the Central Bank of Ireland for a newly established Irish company. Bryan McSharry, chief executive of Moneycorp’s European business, said the licences ensured it could “continue to support our existing customer base, continue to grow our business in Ireland and expand our business across the EU in a post-Brexit environment”. They are: Payments Firms: AIB Merchant Services, Western Union, Fexco, CurrencyFair.com, TransferMate Global Payments, #Fire, CUSOP (Payments) Ltd, #PrimaFinance, Avantcard, Barclaycard, #Chasepaymentech, Google Pay, #smallworld, AFEX, BUREAU BUTTERCRANE LTD, Remitly, J.P. Morgan, Circit.io, Xpress Money, CRIF & Finclude (fka. Verge.Capital) Emoney Firms: EML, Facebook, Soldo, Optal, Paysafe Group, paysafecard.com, Prepaid Financial Services Limited (PFS), #foreigncurrencydirect, Stripe, Coinbase. One4all Group, Payoneer, Square and Moneycorp. Congratulations Moneycorp and Square and welcome to the thriving regulated Irish fintech ecosystem. If you are looking to get authorised in Ireland as an emoney or payments firm, see these Authorisation Guides. Read Moneycorp's press release below. Moneycorp secures its E-Money and MiFID licences in Ireland
New Irish entity, licenced by Central Bank of Ireland, to drive expansion across EU Moneycorp to build on €3 billion of transactions executed for Irish clients in 2019 Dublin, 1 July 2020 | Moneycorp Group, the global foreign exchange and payments business has been granted its Electronic Money Institution (E-Money) and MiFID licences by the Central Bank of Ireland (CBI), further bolstering its offering and expansion in the European Union (EU). Moneycorp is one of the world’s largest specialist foreign exchange companies, serving corporates and individuals across multiple channels since 1979. Headquartered in London, Moneycorp opened its Dublin office in 2013 to provide corporate clients with foreign exchange and payment services over its market leading on-line platform as well as directly from its Dublin dealing room. Since launch, the Dublin office has operated as a branch of the Group’s UK regulated entities, however, as part of Moneycorp’s strategic response to Brexit and wider market developments, it has now secured its E-money and MiFID licences from the CBI for a newly established Irish company; Moneycorp Technologies Limited (MTL). Bryan McSharry, CEO of Moneycorp’s European business, said: “We are delighted to have secured both E-money and MiFID licences from the Central Bank of Ireland. This ensures we can continue to support our existing customer base; continue to grow our business in Ireland; and expand our business across the EU in a post Brexit environment.” “Since launching in Dublin in 2013, we have built a strong corporate and individual customer base of Irish clients – based on our ability to provide best in class foreign exchange services across our market-leading technology platform. We completed €3 billion of transactions for Irish clients in 2019 and we will build on that in 2020 and beyond. Our CBI licences will enable us to continue to expand our business and headcount in Ireland and offer our market-leading service to a vastly increased customer base across the EU.” About Moneycorp Group Moneycorp Group is a global foreign exchange and payments business with offices in the UK, USA, Brazil, Hong Kong, Spain, Gibraltar, Romania, Australia, the UAE and Ireland. With a forty year record of outstanding customer service, today the Moneycorp group serves the growing foreign exchange and payments needs of global businesses, importers and exporters as well as personal clients. W: www.moneycorp.com L: linkedin.com/company/moneycorp/ T: @moneycorp I: instagram.com/moneycorp/ |
© CompliReg.com Dublin 2, Ireland ph +353 1 639 2971
| www.complireg.com | officeATcomplireg.com [replace AT with @]
| www.complireg.com | officeATcomplireg.com [replace AT with @]